


Next: Shock
Up: Hazard Areas
Previous: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Contents
- Establish large bore peripheral lines and if appropriate central venous
access
- Take blood for FBC, U&E, Creatinine, LFTs, Coagulation screen, G&H,
GXM if high risk i.e.
- Age
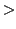 60 years
60 years
- Haemodynamically unstable (Systolic BP
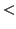 100 mmHg, Pulse
100 mmHg, Pulse 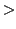 100)
100)
- Hb
 10 g/dl on admission
10 g/dl on admission
- Significant major organ disease
- Pass a nasogastric tube
- Pass urinary catheter and measure hourly urine output, see
section 9.5
- Infuse/Transfuse as needed to maintain red cell mass and to correct
volume and coagulation defects
- Endoscope all patients within 24 hours. Gastroenterology consult
regarding sclerotherapy
- Endoscope within 12 hours if
- high risk (as above)
- re-bleed
- greater than 4 units of blood or plasma expander required to
correct acute blood loss
- Platelets should be given in patients with renal failure or bleeding
secondary to aspirin or NSAIDs regardless of platelet count
- FFP is given if transfusion exceeds 4 units of packed red blood cells
- Keep patient warm
One unit of packed red blood cells (400 ml) gives l gram or 3% increase in
Haematocrit. One pool of platelets increases platelet count by
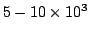 , give after 8 units of packed cells.
Packed cells have maximum 10 days shelf life and decreases by 10% per day
from the outset One unit of fresh frozen plasma (FFP) is given for every 4-6
units of packed red blood cells transfused, it gives all clotting factors
except factor V and VII.
, give after 8 units of packed cells.
Packed cells have maximum 10 days shelf life and decreases by 10% per day
from the outset One unit of fresh frozen plasma (FFP) is given for every 4-6
units of packed red blood cells transfused, it gives all clotting factors
except factor V and VII.



Next: Shock
Up: Hazard Areas
Previous: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Contents
Adrian P. Ireland
 60 years
60 years
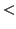 100 mmHg, Pulse
100 mmHg, Pulse 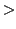 100)
100)
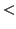 10 g/dl on admission
10 g/dl on admission