


Next: Preoperative Care
Up: Medical problems in surgical
Previous: Hyponatreamia
Contents
- Causes
- Infection; chest, urine, wound, meningitis
- Drugs; especially sedatives, analgesics, psychotropics,
steroids, alcohol and illicit drugs
- Metabolic disorder; electrolyte disturbances, abnormal blood
glucose, acid-base disturbances
- Hypoxia
- Alcohol withdrawal (2-5 days after hospital admission)
- Vascular; cerebrovascular accident - haemorrhage or infarction,
or myocardial infarct
- Head injury; subdural haematoma
- Investigations
- it is VITAL to exclude and treat, potentially reversible cause
- review medical and drug history
- Examine patient
- Bloods - FBC, U&E, glucose, Ca
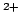 , phosphate, LFT
, phosphate, LFT
- Urine for microscopy C&S, blood cultures
- ABG
- CXR
- CT brain may be required
Adrian P. Ireland
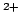 , phosphate, LFT
, phosphate, LFT