


Next: Confusion
Up: Medical problems in surgical
Previous: Hyperkalaemia
Contents
- Causes
- Most common cause is diuretics
- If urinary Na
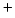
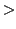 20 mmol/L - Addison's, renal failure (early
stage), diuretic excess, osmolar diuresis (raised glucose, urea)
20 mmol/L - Addison's, renal failure (early
stage), diuretic excess, osmolar diuresis (raised glucose, urea)
- If urinary sodium
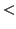 20 mmol/L - Diarrhoea, vomiting, fistula,
burns, small bowel obstruction
20 mmol/L - Diarrhoea, vomiting, fistula,
burns, small bowel obstruction
- If patient is oedematous -- nephrotic syndrome, cardiac
failure, liver cirrhosis, renal failure
- If urine osmolality is
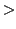 500 mmol/kg - inappropriate ADH
500 mmol/kg - inappropriate ADH
- Investigations
- U&E, urinary spot sodium, plasma and urinary osmolality
- Management
- Aim for gradual increase in plasma Na
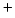
- If dehydrated - and kidney function good, give 0.9% saline.
- If not dehydrated - and Na
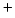
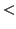 125 mmol/L, restrict water to 0.5 to
1 litre/day if tolerated. Consider Frusemide 40-80 millegrammes/24 hour
125 mmol/L, restrict water to 0.5 to
1 litre/day if tolerated. Consider Frusemide 40-80 millegrammes/24 hour
Adrian P. Ireland
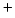
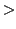 20 mmol/L - Addison's, renal failure (early
stage), diuretic excess, osmolar diuresis (raised glucose, urea)
20 mmol/L - Addison's, renal failure (early
stage), diuretic excess, osmolar diuresis (raised glucose, urea)
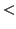 20 mmol/L - Diarrhoea, vomiting, fistula,
burns, small bowel obstruction
20 mmol/L - Diarrhoea, vomiting, fistula,
burns, small bowel obstruction
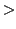 500 mmol/kg - inappropriate ADH
500 mmol/kg - inappropriate ADH
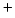
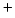
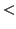 125 mmol/L, restrict water to 0.5 to
1 litre/day if tolerated. Consider Frusemide 40-80 millegrammes/24 hour
125 mmol/L, restrict water to 0.5 to
1 litre/day if tolerated. Consider Frusemide 40-80 millegrammes/24 hour