


Next: Respiratory distress
Up: Medical problems in surgical
Previous: Medical problems in surgical
Contents
- History and examination
- Nature of the pain, radiation and associations
- rapid examination to exclude hypotension, note the presence of
murmurs and to identify and treat acute pulmonary oedema
- Secure iv access
- 12 lead ECG and continuous monitoring for dysrhythmias
- Give
- Oxygen 100% (unless history of severe COAD)
- GTN spray 2 puffs SL
- Diamorphine 2.5-5 millegrammes IV PRN for pain relief
- Metoclopramide 10 millegrammes IV TDS for nausea
- Take blood for
- FBC and U&E; supplement K
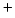 to maintain at 4-5 mmol/L
to maintain at 4-5 mmol/L
- Glucose; may be increased acutely post myocardial infarction
- Cardiac enzymes; Changes start at 4 hours post myocardial infarction
- Troponin test; levels remain elevated up to 2 weeks post myocardial infarction,
elevation is specific marker for myocardial infarction
- CXR (portable)
- to assess cardiac size and pulmonary oedema
- Differential diagnosis
- Pericarditis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Esophageal reflux, spasm or rupture
- Biliary tract disease
- Pancreatitis
- Perforated peptic ulcer disease
- Dissecting aortic aneurysm
- Fracture ribs
- Costochondritis



Next: Respiratory distress
Up: Medical problems in surgical
Previous: Medical problems in surgical
Contents
Adrian P. Ireland
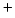 to maintain at 4-5 mmol/L
to maintain at 4-5 mmol/L