



Next: Ischaemia-reperfusion injury
Up: Basic principles
Previous: Endothelial permeability
Index
Endothelial dysfunction is present when there is an inappropriate alteration
with respect to perservation of organ function. Some of the clinical areas
where endothelial function and dysfunction are important are
ischemia-reperfusion injury, endotoxemia, diabetes, immuno-logical rejection
and dyslipidaemia.
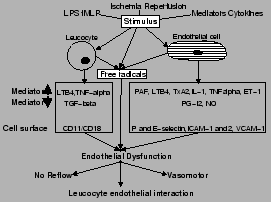
Figure 6:
Patho-physiology of microvascular dysfunction in ischemia-reperfusion injury ,
endotoxemia, diabetes, immunological rejection and dsylipidaemia. External
stimuli result in release of free radicals and endothelial and/or leucocyte
activation with alterations in inflammatory mediators, cytokines and
expression of integrins, selectins and members of the immuno-globulin
super-family. This is manifest as endothelial dsyfunction (no-reflow
phenomenum, increased leucocyte adhesion and migration and vasomotor
dsyfunction).
 |
The core pathophysiology of microvascular and endothelial dysfunction in these
conditions is outlined in figure 6.
The pathophysiology is similar despite the stimulus so ischaemia reperfusion
injury will be used to describe the process.
Adrian P. Ireland
