A mutation in CD18 results in defective ![]() integrin function and is
clinically manifest as LAD syndrome (Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency).
integrin function and is
clinically manifest as LAD syndrome (Leukocyte Adhesion Deficiency).
- CD102
- ICAM-2
- CD106
- VCAM-1
- CD11a
- Subunit of
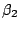 integrin LFA-1
integrin LFA-1
- CD11b
- Subunit of
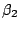 integrin MAC-1
integrin MAC-1
- CD11c
- Subunit of
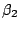 integrin P150
integrin P150
- CD18
- Subunit of
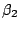 integrins LFA-1, MAC-1, P150
integrins LFA-1, MAC-1, P150
- CD31
- PECAM-1
- CD34
- Ligand for L-Selectin
- CD50
- ICAM-3
- CD54
- ICAM-1
- CD62E
- E-Selectin
- CD62L
- L-Selectin
- CD62P
- P-Selectin
Member of the immunoglobulin superfamily which plays a role in endothelial leucocyte interaction. It weighs 55-65 Kd, is located on resting lymphocytes, monocytes and endothelial cells. It binds to CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1).
Member of the immunoglobulin superfamily which plays a role in endothelial leucocyte interaction It weighs 130 Kd, is located on thymocytes and binds to CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) on leucocytes.
Patients with LAD, are susceptible to recurrent bacterial infections due to the inability to effectively recruit granulocytes.
Production of the harmful free radicals is limited by the supply of oxygen. This is in contrast to the situation in parenchymal ane endothelial cells where production of these reactive species is catalysed by xanthine oxidase and depends on the availability of the hypoxanthine substrate.
Inflammatory mediator formed from a membrane phospholipid by a variety of cells including, platlets, endothelial cells and leucocytes.
Induces shedding of L-selectin from leucocytes that have become adherent.
Binds to a cell surface receptor to induce expression of Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18,
![]() integrin) which is stored in granules in granulocytes and
macrophages. Expression of Mac-1 increased leucocyte adhesion and
transmigration. Transmigration will increase vascular permeability inducing
oedema.
integrin) which is stored in granules in granulocytes and
macrophages. Expression of Mac-1 increased leucocyte adhesion and
transmigration. Transmigration will increase vascular permeability inducing
oedema.
Stimulates formation of oxygen free radicals and release of myeloperoxidase and lactoferrin.
Hypoxia induces endothelial cells to release PAF and increase expression of ICAM-1.
It is locate on the endothelium, leucocytes and platlets.
Product of arachadinoic acid metabolism via the cyclo-oxygenase pathway. Prostaglandin H2 is a potent vaso constrictor, that is normally produced by endothelial cells.
Product of arachadinoic acid metabolism via the cyclo-oxygenase pathway. Prostaglandin I2 is also know as prostacyclin. It is a potent vaso dilator, that is normally produced by endothelial cells.
- E-Selectin
- Also known as CD62E, ELAM-1.
Molecular weight is 140 Kd. Located in the endothelium, the main ligand is the carbohydrate derivitive sialyated Lewis. It is responsible for sialated Lewis mediated leucocyte rolling.
- L-Selectin
- Leucocyte selectin, also known as CD62L, LAM-1, LECAM-1.
Molecular weight is 150 Kd. Located in B, T, NK cells and Monocytes. The main ligand is the carbohydrate derivitive sialyated Lewis. It binds to CD34 and is responsible for glycam mediated leucocyte rolling.
- P-Selectin
- Platlet selectin, also known as CD62P, PADGEM.
Glycoprotein with molecular weight of 140 Kd. It is located in platlets in
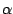 granules and in the Weibel-Palade body
in endothelial cells.
The main ligand is the carbohydrate derivitive sialyated Lewis.
It is responsible for monocyte and leucocyte rolling.
granules and in the Weibel-Palade body
in endothelial cells.
The main ligand is the carbohydrate derivitive sialyated Lewis.
It is responsible for monocyte and leucocyte rolling.
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD106) , member of the immunoglobulin
superfamily which plays a role in endothelial leucocyte interaction. It weighs
100-110 Kd and is located on endothelial cells. Its main ligand on the
leucocyte is VLA-4, a ![]() integrin (
integrin (
![]() ). Expression of
VCAM-1 increases adhesion of lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and
basophils. Some cancer cells particularly melanoma appear to use VCAM-1 to
bind to the endothelium.
). Expression of
VCAM-1 increases adhesion of lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils and
basophils. Some cancer cells particularly melanoma appear to use VCAM-1 to
bind to the endothelium.
Production of the harmful free radicals is limited by the supply of hypoxanthine, when the substrate is exhausted, no more free radicals are produced. This is in contrast to the situation in neutrophils where production of these reactive species is catalysed by NADPH Oxidase and depends on the availability of oxygen. The enzyme may be inhibited by allopurinol.